 |





Triad is a Federal/State Interagency Partnership
|
 |
Training Classes and Materials
Information on Triad training classes and associated presentation materials are available via this section.
Upcoming Internet Seminars
- From Cells to Solutions: Emerging Tools for Studying Health and Disease — Session I – The NIEHS Superfund Research Program (SRP)
January 9, 2026, 1:00PM-3:00PM EST, 18:00-20:00 GMT
The National Institute of Environmental Health Sciences (NIEHS) Superfund Research Program (SRP) is hosting a Risk e-Learning webinar series focused on the use of innovative, human-relevant technologies to better characterize the biological effects of chemicals.
New technologies, including advanced cell-based assays, organoids, and computational modeling approaches, are expanding the toolbox researchers use to answer previously difficult or unanswerable questions. Presenters will discuss how these emerging methodologies are being applied to uncover mechanistic insights, improve predictive accuracy for human health outcomes, and refine risk assessment frameworks.
The first session, titled Multi-Cellular Systems, Modeling, and Simulations to Advance Environmental Health Research, will feature four speakers discussing how cell-based systems, modeling, and simulations can improve researchers' understanding of complex biomedical topics, such as how chemicals interact inside the body or the cause of birth defects. Speakers include:- Margaret Ochocinska, Ph.D., National Institutes of Health
- Brian Johnson, Ph.D., Michigan State University
- Rebecca Fry, Ph.D., University of North Carolina
- Jon Chorover, Ph.D., University of Arizona
To learn more about and register for the other sessions in this webinar series, please see the SRP site.
 http://www.clu-in.org/live/ http://www.clu-in.org/live/
- From Cells to Solutions: Emerging Tools for Studying Health and Disease — Session II – The NIEHS Superfund Research Program (SRP)
January 16, 2026, 12:00PM-2:00PM EST, 17:00-19:00 GMT
The National Institute of Environmental Health Sciences (NIEHS) Superfund Research Program (SRP) is hosting a Risk e-Learning webinar series focused on the use of innovative, human-relevant technologies to better characterize the biological effects of chemicals.
New technologies, including advanced cell-based assays, organoids, and computational modeling approaches, are expanding the toolbox researchers use to answer previously difficult or unanswerable questions. Presenters will discuss how these emerging methodologies are being applied to uncover mechanistic insights, improve predictive accuracy for human health outcomes, and refine risk assessment frameworks.
The second session, titled 3D Models and Technologies to Illuminate Biological Effects of Contaminants, will feature three speakers discussing 3D models and other technologies to better understand how contaminants like polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons and endocrine-disrupting compounds affect DNA, placental function, and asthma. Speakers include:- Bevin Engelward, Sc.D., Massachusetts Institute of Technology
- Susan Tilton, Ph.D., Oregon State University
- Arum Han, Ph.D., Texas A&M University
To learn more about and register for the other sessions in this webinar series, please see the SRP site.
 http://www.clu-in.org/live/ http://www.clu-in.org/live/
- From Cells to Solutions: Emerging Tools for Studying Health and Disease — Session III – The NIEHS Superfund Research Program (SRP)
January 21, 2026, 1:00PM-3:00PM EST, 18:00-20:00 GMT
The National Institute of Environmental Health Sciences (NIEHS) Superfund Research Program (SRP) is hosting a Risk e-Learning webinar series focused on the use of innovative, human-relevant technologies to better characterize the biological effects of chemicals.
New technologies, including advanced cell-based assays, organoids, and computational modeling approaches, are expanding the toolbox researchers use to answer previously difficult or unanswerable questions. Presenters will discuss how these emerging methodologies are being applied to uncover mechanistic insights, improve predictive accuracy for human health outcomes, and refine risk assessment frameworks.
The third and final session, titled Innovative Methods for Understanding Chemical Toxicity, will feature three speakers discussing innovative approaches to understanding the dose at which chemicals trigger biological responses and the mechanisms behind them. Speakers include:- Ana Maretti Garcia, Ph.D., University of Southern California
- Guru Ulaganathan, Duke University
- Weihseuh A. Chiu, Ph.D., Texas A&M University
To learn more about and register for the other sessions in this webinar series, please see the SRP site.
 http://www.clu-in.org/live/ http://www.clu-in.org/live/
- ITRC: Introduction to Hydrocarbons – Interstate Technology and Regulatory Council
January 13, 2026, 1:00PM-3:00PM EST, 18:00-20:00 GMT
Petroleum is a complex mixture of many compounds. Regulatory and technical guidance documents commonly focus on the hydrocarbon components of that mixture, or perceived risks that they present. However, focusing on a specific area of concern often causes practitioners to overlook other aspects of a release. For example, concerns related to exposure to total petroleum hydrocarbons (TPH) risks may be overlooked while pursuing concerns related to light non-aqueous phase liquid (LNAPL) recovery or petroleum vapor intrusion (PVI).
This class is designed to provide a basic overview of hydrocarbon behavior in the subsurface and how to scientifically assess concerns arising from the release of petroleum products into the environment. It will highlight key issues that help identify and manage TPH, LNAPL, and PVI risks together. Key concepts will include: - Fundamentals of petroleum hydrocarbons
- Petroleum chemistry
- How TPH, LNAPL, and PVI are related
- Building an integrated conceptual site model (CSM)
- What is a CSM…what is its purpose?
- When is a CSM complete?
- Identifying and managing the risks from petroleum hydrocarbons
- Defining LNAPL risks based on acute, saturation, composition, or aesthetic concerns
- Emphasize the importance of biodegradation in risk management decision making
- How to select remedial goals and remedies that align with your goals
This course is based upon three separate Guidance Documents developed by ITRC that address the course content in detail:
 http://www.clu-in.org/live/ http://www.clu-in.org/live/
- ITRC: Managed Aquifer Recharge (MAR) – Interstate Technology and Regulatory Council
January 15, 2026, 1:00PM-3:00PM EST, 18:00-20:00 GMT
The ITRC Managed Aquifer Recharge (MAR-1) Training is intended for state regulators and stakeholders who may not be familiar with the opportunities and challenges associated with MAR. It provides a basic understanding of MAR concepts, along with case studies, that showcase examples of successful MAR applications. For those who are familiar with MAR, the training gives an overview of the components of the MAR process along with the important considerations associated with each component necessary for the design and implementation of a MAR project. It is important to understand that MAR is an area of active research and expanding practical applications, and that this management process is continuing to evolve with time.The combination of climate change and growing demand for fresh water has resulted in an increase in the vulnerability and scarcity of freshwater supplies around the world. The need for fresh water to grow crops and provide for the welfare of the general population, economic growth, and ecosystems is becoming more acute. In the past 50 years, the amount of water withdrawn for human use has tripled. MAR is becoming an increasingly important method for improving and supplementing subsurface freshwater storage and ecosystems with an additional benefit of reducing flood risk, managing stormwater, mitigating subsidence, and controlling saltwater intrusion. Training Objectives - Understand MAR and its applications.
- Recognize MAR as a process rather than a single technology.
- Acknowledge that MAR can be widely applied.
- Understand MAR's role in the future for addressing water supply resilience and climate impacts.
Training Goals - Provide a model of the MAR process illustrating the primary components and their interaction.
- Provide an overview of the applications of MAR and the role in addressing climate change impacts through sustainability and resilience in water resources management.
- Provide information on each component of MAR and the critical considerations for each component in the design of a MAR project.
- Reference case studies illustrating the various applications of MAR.
After the MAR Training, the audience will have the tools necessary to understand MAR and how it can be used as a water resource management tool that encompasses a wide variety of water sources, recharge methods, and storage management practices. The audience will develop an understanding of MAR and its importance in achieving sustainability, resilience, and the far-reaching benefits of MAR related to water supply and quality, mitigation of saltwater intrusion, flood control, and ecological habitats. This training will provide information about the components of a MAR project to help regulators, practitioners, and stakeholders in the development and review of a MAR project. Recommended Reading: Participants are strongly encouraged to review the ITRC Managed Aquifer Recharge document prior to participating in the training class.
 http://www.clu-in.org/live/ http://www.clu-in.org/live/
- ITRC: Contaminants of Emerging Concern (CEC) Identification Framework – Interstate Technology and Regulatory Council
January 22, 2026, 1:00PM-3:00PM EDT, 18:00-20:00 GMT
In 2023, the ITRC Contaminants of Emerging Concern (CEC) Framework was published to help environmental regulatory agencies and other stakeholders identify, evaluate, and manage CEC's while acknowledging uncertainties in their environmental fate and transport, receptor exposure, and/or toxicity. Such an approach can be conducive to improved allocation of regulatory response resources and provide a foundation for communicating potential risk to stakeholders. The ITRC framework is comprised of a white paper and four associated fact sheets. In the white paper, CEC are defined as: "substances and microorganisms including physical, chemical, biological, or radiological materials known or anticipated in the environment, that may pose newly identified risks to human health or the environment." The framework is meant to help environmental regulatory agencies and other stakeholders by providing examples of CEC monitoring programs and guiding the user through the process of identifying CEC key characteristics, how to communicate real and perceived risk from CEC to the public, and how laboratory analytical methods can be used in the identification process. The ITRC CEC training presents this entirely new framework for identification, prioritization, and communication of CEC. This course includes the following topics: - An overview of the framework, how and why it was developed, the factors that influence the creation of CEC management units at the state level, and a listing of existing CEC monitoring programs.
- A discussion of key variables that may be used as criteria to identify and prioritize CEC for response actions. This portion of the course includes a case study that illustrates how the identification and prioritization process works with an "unknown" chemical CEC.
- Practices and methods for stakeholder messaging and how to share incomplete information on CEC that could impact human health and the environment. This portion of the short course builds upon the ITRC Risk Communication Toolkit by providing additional detail addresses communications plans, message maps, and audience identification.
- A paradigm for how laboratory methods can be used to identify CEC ranging from:
- "Is compound X in the sample and at what concentration?" (i.e., known knowns) to
- "Which compounds from the list are in this sample?" (i.e., known unknowns) to
- "What is in the sample?" (i.e., unknown unknowns).
CEC are typically compounds or substances whose occurrence or effect is unknown but may or may not be understood through similar compounds or substances. This module includes a discussion of the use of targeted and untargeted analysis to identify a CEC. Participants will learn the elements of the CEC framework and gain an understanding of the framework application from case studies. Participants are encouraged to review the ITRC CEC Framework prior to the class.
 http://www.clu-in.org/live/ http://www.clu-in.org/live/
- ITRC: PFAS Chemistry Explained – Interstate Technology and Regulatory Council
January 27, 2026, 1:00PM-3:00PM EST, 18:00-20:00 GMT
The Interstate Technology & Regulatory Council (ITRC) is presenting a training on the basics of per- and polyfluoroalkyl substances (PFAS) chemistry. This training supplements the ITRC PFAS Introductory training and ITRC Beyond the Basics Training sessions. You can find ITRC PFAS training resources online at https://pfas-1.itrcweb.org/pfas-training/.
PFAS are an emerging group of contaminants that present unique challenges in many areas including: widespread use and presence in the environment, sampling and analysis, fate and transport, and remedial approaches. This training session will provide PFAS practitioners with an understanding of the unique aspects of PFAS chemistry that guide fate and transport, treatment, regulations, and decision-making on PFAS sites.
Key focus areas of the training include the following:- Why are PFAS different from other organic chemicals?
- How are PFAS defined?
- How are PFAS manufactured and why does that matter?
- What are the differences between perfluoroalkyl and polyfluoroalkyl substances?
- What are the naming conventions used for the different types of PFAS?
- How are short-chain and long-chain perfluoroalkyl acids (PFAAs) defined?
- What are precursors and why are they important?
- What are some of the unique chemical properties of PFAS and why do they matter?
Resources and further details included in this training are in the ITRC Guidance Document (PFAS-1).
 http://www.clu-in.org/live/ http://www.clu-in.org/live/
- ITRC: Microplastics – Interstate Technology and Regulatory Council
February 12, 2026, 1:00PM-3:00PM EST, 18:00-20:00 GMT
In response to one of the biggest emerging environmental concerns, ITRC formed the Microplastics Team in 2021 to develop the Microplastics Guidance Document. Plastics have become pervasive in modern life and are now used in a wide range of commercial and industrial applications. Microplastics may result from the degradation and fragmentation of larger plastics, or they may be intentionally produced for specific applications and products. Regardless of their origin, microplastics are now ubiquitous in our environment. Because of their small size and pervasiveness in the environment, microplastics, along with any other contaminants which are adhered to the microplastics, may be inadvertently consumed by humans and other organisms.
The online ITRC Guidance Document is geared toward an audience with reasonable level of scientific understanding, but not microplastic-specific knowledge. The guidance provides a user with information on microplastics and the state of the applied science without having to go to the scientific literature.
The target audience for the guidance and this training course includes state regulators and environmental consultants, as well as community and tribal stakeholders.
The guidance and this associated training course uses a conceptual site model to navigate microplastics in the environment and explore the following general areas:- An introduction to microplastics, their sources, and worldwide distribution
- The pathways through which microplastics can enter and travel in the environment and their distribution in various media (water, soil, sediment, air, and biota)
- A current look at the most common techniques and best practices for sampling and analyzing microplastics
- Potential human health and ecological risks associated with microplastics in the environment
- An overview of existing regulations related to microplastics and macroplastics at the state, federal, and international levels
- Examples of prevention and mitigation strategies and best management practices to reduce microplastics from entering the environment and the emerging technologies to abate, treat, and remediate microplastics once they exist in the environment
- Identification of data gaps and the need for further research
- Several case studies illustrating a range of current microplastics-related topics
Prior to attending the training class, participants are encouraged to view the associated ITRC Microplastics Guidance Document.
 http://www.clu-in.org/live/ http://www.clu-in.org/live/
- Sediment Cap Chemical Isolation Training – Interstate Technology and Regulatory Council
February 17, 2026, 1:00PM-3:00PM EST, 18:00-20:00 GMT
In 2023, ITRC published the Sediment Cap Chemical Isolation Guidance to supplement the 2014 Contaminated Sediments Remediation Guidance with the goal of improving consistency in sediment cap performance outcomes. Sediment capping is a commonly selected remediation approach and numerous designs have been completed. Previous cap designs have been evaluated in multiple ways, and these varying approaches have led to some differences in selection of chemical design criteria, construction tolerance specifications, and monitoring/maintenance objectives for sites with similar characteristics and contaminants, leading to different expectations for long-term performance and reliability.
The ITRC Sediment Cap Chemical Isolation Guidance provides a framework for the design, construction, and long-term monitoring of the chemical isolation function of sediment caps. The framework consists of an iterative design process informed by site-specific data that balances achievement of chemical design criteria, physical design constraints, constructability and permitting requirements. In addition, the guidance summarizes key construction considerations and presents a recommended approach for monitoring and evaluating long-term chemical isolation performance. The recommended framework presented in the Sediment Cap Chemical Isolation Guidance is illustrated below.
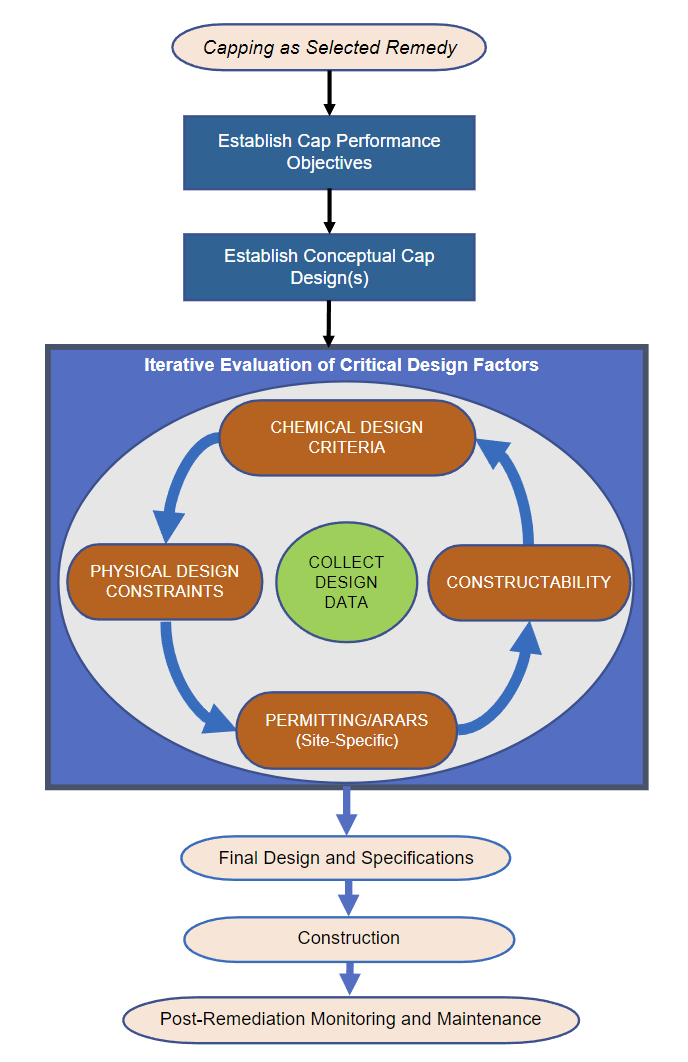
The Sediment Cap Chemical Isolation Training will cover several key elements of the recommended framework, including:
- A capping overview that summarizes objectives of capping, role of the chemical isolation layer, and generic cap types and compositions.
- A discussion of performance objectives and design concepts that includes the selection of chemical isolation performance targets criteria and development of design criteria while considering the site setting and conceptual site model elements.
- An overview of chemical isolation layer modeling tools and discussion of their applicability to support chemical isolation design, important model input parameters, and the impact of uncertainty and sensitivity of modeling results.
- A summary of chemical isolation construction considerations, including an overview of available construction methods and tolerances and quality assurance and quality control measures.
- A discussion of cap performance monitoring and maintenance objectives and approaches that include developing monitoring objectives to assess chemical isolation performance and methods for guiding long-term maintenance decisions.
We encourage participants to review the ITRC Sediment Cap Chemical Isolation Guidance (SD-1) before and after the training to become familiar with the topics and recommendations discussed during the training. This training is intended for all environmental professionals working in the field of sediment capping projects, including regulators and other government agency staff, consultants, project stakeholders, and industry.
 http://www.clu-in.org/live/ http://www.clu-in.org/live/
- Vapor Intrusion Mitigation (VIM-1) - A Two Part Series: Session 1 – Interstate Technology and Regulatory Council
February 24, 2026, 1:00PM-3:00PM EST, 18:00-20:00 GMT
ITRC's Vapor Intrusion Mitigation training is a series of eight (8) modules, presented over two sessions. If you took the ITRC VIM series previously, the content has stayed the same, but the new course directs people to the Vapor Intrusion (VI) Toolkit resources published in January 2026 by ITRC.
The Vapor Intrusion Mitigation training series provides an overview of VIM and presents information from the 2026 ITRC VI Toolkit (which includes fact sheets, technology information sheets, and checklists) (to be published in January 2026).
- Session 1:
- Introduction & Overview of Vapor Intrusion Mitigation Training Team
- Conceptual Site Models for Vapor Intrusion Mitigation
- Community Engagement During Vapor Intrusion Mitigation
- Rapid Response & Ventilation for Vapor Intrusion Mitigation
- Remediation & Institutional Controls
- Session 2:
- Active Mitigation Approaches
- Passive Mitigation Approaches
- System Verification, OM&M, Curtailment and Shutdown
When certain contaminants or hazardous substances are released into the soil or groundwater, they may volatilize into soil vapor. VI occurs when these vapors migrate up into overlying buildings and contaminate indoor air. The ITRC VI Toolkit combines the previous ITRC VI-related guidance documents (VI 2007, PVI 2014, VIM-1 2020), along with updates, into one comprehensive resource toolkit (including fact sheets, technology information sheets and checklists) published in January 2026.
After the Vapor Intrusion Mitigation series, you should understand: - How to locate and utilize the relevant document, fact sheets, technology information sheets, and checklists
- The importance of a VI mitigation conceptual site model
- How community engagement for VI mitigation differs from other environmental matters
- When to implement rapid response for VI and applicable methodologies
- The differences between remediation, mitigation, and institutional controls
- Available technologies for active and passive mitigation, and design considerations for various approaches
- How/when/why different mitigation technologies are appropriate
- How to verify mitigation system success, address underperformance, and develop a plan for curtailment of a mitigation system and shutdown
We encourage you to use the ITRC VI Toolkit (coming January 2026) and these training modules to learn about VI mitigation and how you can apply these best practices to improve decision-making at your sites. For regulators and other government agency staff, this understanding of VI mitigation can be incorporated into your own programs.
While the training makes every effort to keep the information accessible to a wide audience, it is assumed that the participants will have some basic technical understanding of chemistry, environmental sciences, and risk assessment. As with other emerging contaminants, our understanding of VI mitigation continues to advance. This training provides the participants with information on areas where the science is evolving and where uncertainty persists.
 http://www.clu-in.org/live/ http://www.clu-in.org/live/
PFAS & Biosolids: Sources, Occurrence, Transport, and Treatment – Interstate Technology and Regulatory Council
February 26, 2026, 1:00PM-3:00PM EST, 18:00-20:00 GMT
This ITRC training will provide information on the current understanding of PFAS and biosolids, focusing on land application. It builds on the earlier topics covered in the PFAS 101 training.
This training will provide information on potential sources of PFAS in biosolids, the implications of PFAS associated with land-applied biosolids, including leaching and associated risks, and a conceptual site model. It will also cover the nature and extent of PFAS, field and laboratory considerations when assessing land application sites, factors controlling PFAS mobility, PFAS treatment options for biosolids, and PFAS uptake by plants and animals in these settings, along with approaches to modeling that uptake.
Resources and further details for the topics included in this training are available in the ITRC PFAS-1 guidance document, specifically in Sections 1.7, 2, 4, 5, 8, 10, 12, and 17.3, as well as in the Regulatory Programs Table.
Key topics will include: - Understanding the Sources and Types of PFAS
- Considerations for Evaluating Nature & Extent of PFAS Contamination at Land Application Sites
- Evaluating Fate and Transport of PFAS in the Environment from Land-Applied Biosolids
- Evaluating and Modeling Risk from PFAS in Agricultural Settings
- Evaluating Treatment and Management Options for PFAS in Biosolids
 http://www.clu-in.org/live/ http://www.clu-in.org/live/
ITRC PFAS Introductory Training – Interstate Technology and Regulatory Council
March 5, 2026, 1:00PM-3:00PM EST, 18:00-20:00 GMT
Per- and polyfluoroalkyl substances (PFAS) are a large and complex class of anthropogenic compounds whose prevalence in the environment are an emerging, worldwide priority in environmental and human health. The ITRC PFAS Team, formed in 2017, has prepared readily accessible materials to present PFAS information to stakeholders, regulators, and policy makers. The PFAS team represents a diverse cross-section of expertise and experience working on PFAS.
This training will include emerging science on PFAS, including topics such as Properties of PFAS, Fate and Transport, Sampling and Analysis, and Treatment Technologies. The technical presentations will be focused on those who are relatively new to PFAS. The training will last approximately 90 minutes and include time for questions.
 http://www.clu-in.org/live/ http://www.clu-in.org/live/
ITRC: Reuse of Solid Mining Waste – Interstate Technology and Regulatory Council
March 12, 2026, 1:00PM-3:00PM EDT, 17:00-19:00 GMT
Solid mining waste represents a significant quantity of waste material in the United States and around the world. Solid mining waste has a range of physical and chemical properties that make it both potentially valuable and potentially hazardous to human health and the environment. From a commercial perspective, mining removes most of the primary minerals of interest; however, waste materials can still contain valuable minerals and other materials that can be recovered. The different types of mining sites and potential wastes for reuse provide a significant challenge but also an opportunity for innovation.
Improvements in extraction and mineral processing technologies have occurred over time making it possible to recover minerals present in low concentrations. Interest in trace metals and rare earth elements (REEs) has increased, especially with the drive towards renewable energy sources increasing demand for key minerals required for solar panels and batteries. The reuse of solid mining waste can consist of reprocessing and repurposing the waste for resource recovery or a new application or product. This reuse serves as a solution to two significant needs:- a domestic supply of minerals and materials for sustainable development and national defense purposes
- the reclamation and remediation of land to reduce risks to human and environmental health
The ITRC Reuse of Solid Mining Waste training and guidance document is geared towards state regulators and environmental consultants, mining and manufacturing stakeholders, community and tribal stakeholders, and other who have an interest in the potential reuse of solid mining waste.
The guidance and this associated training course includes:- Mining wastes introduction
- Considerations for reusing mining waste: waste characterization, economic and market considerations, life cycle and risk assessment, regulatory considerations, & stakeholder considerations
- Potential applications for the reuse of solid mining waste: examples of construction, environmental, and industrial reuses
- Review of technologies used in mineral beneficiation and processing
Additionally, the guidance includes several case studies illustrating a range of current mining waste reuse scenarios. Prior to attending the training class, participants are encouraged to view the associated ITRC Reuse of Solid Mining Waste document.
 http://www.clu-in.org/live/ http://www.clu-in.org/live/
Vapor Intrusion Mitigation (VIM-1) - A Two Part Series: Session 2 – Interstate Technology and Regulatory Council
March 17, 2026, 1:00PM-3:00PM EDT, 17:00-19:00 GMT
ITRC's Vapor Intrusion Mitigation training is a series of eight (8) modules, presented over two sessions. If you took the ITRC VIM series previously, the content has stayed the same, but the new course directs people to the Vapor Intrusion (VI) Toolkit resources published in January 2026 by ITRC.
The Vapor Intrusion Mitigation training series provides an overview of VIM and presents information from the 2026 ITRC VI Toolkit (which includes fact sheets, technology information sheets, and checklists) (to be published in January 2026).
- Session 1:
- Introduction & Overview of Vapor Intrusion Mitigation Training Team
- Conceptual Site Models for Vapor Intrusion Mitigation
- Community Engagement During Vapor Intrusion Mitigation
- Rapid Response & Ventilation for Vapor Intrusion Mitigation
- Remediation & Institutional Controls
- Session 2:
- Active Mitigation Approaches
- Passive Mitigation Approaches
- System Verification, OM&M, Curtailment and Shutdown
When certain contaminants or hazardous substances are released into the soil or groundwater, they may volatilize into soil vapor. VI occurs when these vapors migrate up into overlying buildings and contaminate indoor air. The ITRC VI Toolkit combines the previous ITRC VI-related guidance documents (VI 2007, PVI 2014, VIM-1 2020), along with updates, into one comprehensive resource toolkit (including fact sheets, technology information sheets and checklists) published in January 2026.
After the Vapor Intrusion Mitigation series, you should understand: - How to locate and utilize the relevant document, fact sheets, technology information sheets, and checklists
- The importance of a VI mitigation conceptual site model
- How community engagement for VI mitigation differs from other environmental matters
- When to implement rapid response for VI and applicable methodologies
- The differences between remediation, mitigation, and institutional controls
- Available technologies for active and passive mitigation, and design considerations for various approaches
- How/when/why different mitigation technologies are appropriate
- How to verify mitigation system success, address underperformance, and develop a plan for curtailment of a mitigation system and shutdown
We encourage you to use the ITRC VI Toolkit (coming January 2026) and these training modules to learn about VI mitigation and how you can apply these best practices to improve decision-making at your sites. For regulators and other government agency staff, this understanding of VI mitigation can be incorporated into your own programs.
While the training makes every effort to keep the information accessible to a wide audience, it is assumed that the participants will have some basic technical understanding of chemistry, environmental sciences, and risk assessment. As with other emerging contaminants, our understanding of VI mitigation continues to advance. This training provides the participants with information on areas where the science is evolving and where uncertainty persists.
 http://www.clu-in.org/live/ http://www.clu-in.org/live/
PFAS - Practical Approaches for PFAS Fate & Transport Evaluation – Interstate Technology and Regulatory Council
March 26, 2026, 1:00PM-3:00PM EST, 17:00-19:00 GMT
This training will provide information on fate and transport of PFAS in the environment using a hypothetical AFFF release. It builds on the earlier topics covered in the PFAS 101 training. Resources and further details for the topics included in this training are available in the ITRC PFAS-1 guidance document.
Representative PFAS fate and transport pathways/processes will be illustrated, highlighting those that are unique to PFAS and different from other common contaminants. Available methods/approaches of field sampling, laboratory analysis, and data evaluation to characterize these fate and transport pathways/processes will be discussed. Data gaps due to limited available sampling/analysis and data evaluation methods will also be discussed.
The scenario of a hypothetical AFFF release site was chosen based on commonality with typical known environmental releases to present an illustrative framework for regulators and other environmental practitioners on the range of PFAS topics that may be applicable from discovery to closure. This training will be crafted for an audience with some basic understanding of PFAS and that has likely already attended the PFAS 101 training and the ITRC PFAS Beyond the Basics: Fate and Transport, Site Characterization, and Source ID training.
This training will be a site-based, application-oriented training that is built around a specific site narrative. We aim to connect the previous subject-oriented training courses to what practitioners need to think about at a site.
Learning Objectives:- Understand the interrelationships between current ITRC PFAS knowledge topics in the context of a hypothetical scenario.
- Understand representative fate and transport processes at a typical AFFF release site; particular focus will be given to PFAS-specific considerations
- Understand currently available methods/approaches of field sampling, laboratory analysis, and data evaluation for PFAS site characterization, as well as limitations of these methods/approaches
 http://www.clu-in.org/live/ http://www.clu-in.org/live/
PFAS Sorption Based Technologies for Separation & Concentration of PFAS from Water – Interstate Technology and Regulatory Council
April 7, 2026, 1:00PM-3:00PM EST, 17:00-19:00 GMT
Removal of PFAS from water has become an important concern for water utilities; landfill operators; industry professionals; and state, local, and tribal decision makers. Sorption-based technologies, specifically granular activated carbon, ion exchange resins, and foam fractionation have proven to be effective solutions in this area, but choosing the most suitable sorption-based method or system configuration can be daunting. To aid treatment practitioners, the ITRC PFAS team published a technical guidance document titled "Sorption-based Technologies for Separation and Concentration of PFAS from Water" (Section 18 of PFAS-1). This training module is intended to assist in using the information presented in this document by providing an overview of the central topics along with easily digestible summaries of critical information.
This training will be crafted for an audience with some basic understanding of PFAS and that has likely already attended the PFAS 101 training and the ITRC PFAS Beyond the Basics: Fate and Transport, Site Characterization, and Source ID training.
Resources and further details for the topics included in this training are available in the ITRC PFAS-1 guidance document, specifically in Sections 12 and 18.
Learning objectives:- Review operating principles of sorption-based technologies.
- Understand how site conditions and treatment objectives influence technology selection.
- Become familiar with testing methods (from foamability tests to isotherm tests to full-scale demonstration tests) used to verify treatment effectiveness, optimize performance, and compare technologies.
- Identify water quality parameters that may adversely affect sorption-based technologies and the available pretreatment methods to address them
- Learn how test data can be combined with cost and sustainability information to select a specific technology or system configuration.
 http://www.clu-in.org/live/ http://www.clu-in.org/live/
Understanding Vapor Intrusion - Introductory Concepts & Fundamentals - A Two Part Series: Session 1 – Interstate Technology and Regulatory Council
April 30, 2026, 1:00PM-3:00PM EST, 17:00-19:00 GMT
The Vapor Intrusion 101 training series provides an overview of vapor intrusion (VI) and presents information from the 2026 ITRC VI Toolkit (which includes fact sheets, technology information sheets, and checklists) (to be published in January 2026).
This course introduces participants to the fundamentals of vapor intrusion, the process by which vapor-forming chemicals in contaminated soil or groundwater volatilize and migrate into buildings. The course will discuss sources, pathways, and receptors. It will identify and assess VI risks in various settings (residential, commercial, industrial) and familiarize participants with regulatory frameworks and guidelines (e.g., USEPA, state-specific regulations). The participants will gain working knowledge of how to develop a Conceptual Site Model (CSM), design and implement sampling strategies, establish data quality objectives (DQOs), and conduct data and risk evaluations. It will provide an overview of mitigation strategies, including various closure strategies, land use covenants, and institutional controls.
Session 1 will focus on:- What is Vapor Intrusion
- VI Exposure Pathway
- VI in Practice - including common CSMs, Scenarios, and Chemicals
- Potential Limiting Factors for VI - PVI vs Chlorinated VI, Geology, Hydrogeology, and Building Operating Conditions
- How is VI Different & Challenges in Evaluating VI
Session 2 will focus on:- How VI is Different
- How to assess VI - CSM, Sample Collection, Data Interpretation, Risk Assessment, and Project Life Cycle
- Managing VI Risk at a Site - Mitigation, Remediation, Monitoring
- What does Closure look like & Various Exit Strategies
The course will provide connections to the 2026 ITRC VI Toolkit to help the audience understand how to find and use these new resources for VI sites.
 http://www.clu-in.org/live/ http://www.clu-in.org/live/
ITRC: Pump & Treat Optimization – Interstate Technology and Regulatory Council
May 5, 2026, 1:00PM-3:00PM EST, 17:00-19:00 GMT
ITRC's Pump & Treat (P&T) Optimization training aims to summarize existing information and best practices while also developing a systemic and adaptive optimization framework specifically for P&T well-network design and management. P&T systems have been one of the most commonly used methods for hydraulic containment and treatment of contaminated groundwater at sites with large groundwater plumes. This method cleans up groundwater contaminated with dissolved chemicals by pumping groundwater from wells to an above-ground treatment system that removes the contaminants. Optimization of P&T remedies is important for maintaining contaminant removal effectiveness throughout the operation lifetime and managing the system toward an exit strategy. A strategy for routine optimization of P&T remedies is key for maintaining the contaminant removal efficiency of these systems. The primary audience for this training is environmental project decision-makers, which may include federal, state, tribal, and various local agency employees; contractors to these agencies; and potentially liable parties and their engineers and consultants as well as involved stakeholders. Generally, those involved in designing, building and operating, and optimizing pump & treat systems would benefit. The goal of the training is to provide a roadmap for optimizing a P&T system and refining the remedial strategy or shifting toward another remedial approach. Pump & Treat optimization should be systematic and data-based, and the training and document aim to provide tools and direction to assist in this rigorous process. Key Takeaways - Understanding the P&T project lifecycle: evaluation, optimization, and transition, as well as considerations for sustainability, resiliency, and regulatory and stakeholder entities.
- P&T optimization should incorporate adaptive site management.
- P&T systems are influenced by a diverse collection of outside factors, which should be considered throughout the entire optimization process.
- Transition and termination should both be considered during the optimization process.
- Remedial objectives dictate evaluation and optimization efforts for P&T systems..
Prior to attending the training class, participants are encouraged to view the associated ITRC Pump & Treat guidance document .
 http://www.clu-in.org/live/ http://www.clu-in.org/live/
Understanding Vapor Intrusion -Introductory Concepts & Fundamentals - A Two Part Series: Session 2 – Interstate Technology and Regulatory Council
May 12, 2026, 1:00PM-3:00PM EST, 17:00-19:00 GMT
The Vapor Intrusion 101 training series provides an overview of vapor intrusion (VI) and presents information from the 2026 ITRC VI Toolkit (which includes fact sheets, technology information sheets, and checklists) (to be published in January 2026).
This course introduces participants to the fundamentals of vapor intrusion, the process by which vapor-forming chemicals in contaminated soil or groundwater volatilize and migrate into buildings. The course will discuss sources, pathways, and receptors. It will identify and assess VI risks in various settings (residential, commercial, industrial) and familiarize participants with regulatory frameworks and guidelines (e.g., USEPA, state-specific regulations). The participants will gain working knowledge of how to develop a Conceptual Site Model (CSM), design and implement sampling strategies, establish data quality objectives (DQOs), and conduct data and risk evaluations. It will provide an overview of mitigation strategies, including various closure strategies, land use covenants, and institutional controls.
Session 1 will focus on:- What is Vapor Intrusion
- VI Exposure Pathway
- VI in Practice - including common CSMs, Scenarios, and Chemicals
- Potential Limiting Factors for VI - PVI vs Chlorinated VI, Geology, Hydrogeology, and Building Operating Conditions
- How is VI Different & Challenges in Evaluating VI
Session 2 will focus on:- How VI is Different
- How to assess VI - CSM, Sample Collection, Data Interpretation, Risk Assessment, and Project Life Cycle
- Managing VI Risk at a Site - Mitigation, Remediation, Monitoring
- What does Closure look like & Various Exit Strategies
The course will provide connections to the 2026 ITRC VI Toolkit to help the audience understand how to find and use these new resources for VI sites.
 http://www.clu-in.org/live/ http://www.clu-in.org/live/
Top of page
Archived Internet Seminars
Characterization Approaches for Various Types of NAPLs - U.S. EPA Office of Research and Development, Archive of Dec 19, 2024 Seminar
 http://www.cluin.org/live/archive/#20241219
http://www.cluin.org/live/archive/#20241219
SRP Water Innovation - An Integrated Approach to Sustainable Solutions: Session II - Technologies for Water Remediation - NIEHS Superfund Research Program, Archive of Jun 20, 2016 Seminar
 http://www.cluin.org/live/archive/#20160620
http://www.cluin.org/live/archive/#20160620
Implementation of Triad for Petroleum Brownfield's Cleanup and Reuse - US EPA Technology Innovation and Field Services Division, Archive of Jan 26, 2010 Seminar
 http://www.cluin.org/live/archive/#20100126
http://www.cluin.org/live/archive/#20100126
Triad Month Session 7: Dynamic Work Strategies - U.S. EPA Technology Innovation and Field Services Division, Archive of Aug 25, 2009 Seminar
 http://www.cluin.org/live/archive/#20090825
http://www.cluin.org/live/archive/#20090825
Triad Month Session 6: Triad Case Studies - U.S. EPA Technology Innovation and Field Services Division, Archive of Aug 20, 2009 Seminar
 http://www.cluin.org/live/archive/#20090820
http://www.cluin.org/live/archive/#20090820
Triad Month Session 5: Triad Implementation - U.S. EPA Technology Innovation and Field Services Division, Archive of Aug 18, 2009 Seminar
 http://www.cluin.org/live/archive/#20090818
http://www.cluin.org/live/archive/#20090818
Triad Month Session 4: Triad Measurement Techniques - U.S. EPA Technology Innovation and Field Services Division, Archive of Aug 13, 2009 Seminar
 http://www.cluin.org/live/archive/#20090813
http://www.cluin.org/live/archive/#20090813
Triad Month Session 3: Triad During RD/RA - U.S. EPA Technology Innovation and Field Services Division, Archive of Aug 11, 2009 Seminar
 http://www.cluin.org/live/archive/#20090811
http://www.cluin.org/live/archive/#20090811
Triad Month Session 2: Triad Communications and Systematic Planning - U.S. EPA Technology Innovation and Field Services Division, Archive of Aug 6, 2009 Seminar
 http://www.cluin.org/live/archive/#20090806
http://www.cluin.org/live/archive/#20090806
Triad Month Session 1: Introduction to Triad - U.S. EPA Technology Innovation and Field Services Division, Archive of Aug 4, 2009 Seminar
 http://www.cluin.org/live/archive/#20090804
http://www.cluin.org/live/archive/#20090804
Triad: Beyond Characterization to Long-term Management of Groundwater Contaminant Plumes - U.S. EPA Technology Innovation Program, Archive of Sep 12, 2008 Seminar
 http://www.cluin.org/live/archive/#20080912
http://www.cluin.org/live/archive/#20080912
Demystifying the DMA (Demonstration of Method Applicability) - U.S. EPA Technology Innovation and Field Services Division, Archive of Jul 28, 2008 Seminar
 http://www.cluin.org/live/archive/#20080728
http://www.cluin.org/live/archive/#20080728
Management and Interpretation of Data Under a Triad Approach - U.S. EPA Technology Innovation and Field Services Division, Archive of May 22, 2008 Seminar
 http://www.cluin.org/live/archive/#20080522
http://www.cluin.org/live/archive/#20080522
Triad Approach: A New Paradigm for Environmental Project Management - Interstate Technology and Regulatory Council, Archive of Feb 10, 2005 Seminar
 http://www.cluin.org/live/archive/#20050210
http://www.cluin.org/live/archive/#20050210
The Triad Approach to Better Cleanup Projects: Illustrated with the Tree Fruit Case Study - U.S. Army Corps of Engineers and U.S. EPA, Technology Innovation Office, Archive of Jan 23, 2003 Seminar
 http://www.cluin.org/live/archive/#20030123
http://www.cluin.org/live/archive/#20030123
Field-Based Geophysical Technologies Online Seminar - U.S. EPA, Technology Innovation Office, Archive of Dec 12, 2001 Seminar
 http://www.cluin.org/live/archive/#20011212
http://www.cluin.org/live/archive/#20011212
Top of page
Training Presentation Slides
The links below lead to Triad training materials (PowerPoint presentations, video clips, etc.) developed by members of the Triad working group.
- Triad Course Delivery at the National Site Assessment Symposium, June 28, 2004, San Diego, – USEPA, PPT slides for modules of the full-day delivery of training and case studies.
 Is the Triad Approach Really Something New? (Presenter: Deana Crumbling, USEPA) (319 KB) Is the Triad Approach Really Something New? (Presenter: Deana Crumbling, USEPA) (319 KB)
 Triad's Systematic Planning Process (Presenter: Andrianne Saboya, US Navy PWC Environmental Dept.) (206 KB) Triad's Systematic Planning Process (Presenter: Andrianne Saboya, US Navy PWC Environmental Dept.) (206 KB)
 Evolving Conceptual Site Models (CSMs) in Real-time for Cost Effective Projects (Presenter: Kira Lynch, USACE, Seattle District) (8.0 MB) Evolving Conceptual Site Models (CSMs) in Real-time for Cost Effective Projects (Presenter: Kira Lynch, USACE, Seattle District) (8.0 MB)
 Building A Second-Generation Data Quality Model (Presenter: Deana Crumbling, USEPA) (1.7 MB) Building A Second-Generation Data Quality Model (Presenter: Deana Crumbling, USEPA) (1.7 MB)
 Introduction to 3-D Mapping Techniques (Presenter: Timothy Shields, Anteon Corp./US Navy PWC) (6.7 MB) Introduction to 3-D Mapping Techniques (Presenter: Timothy Shields, Anteon Corp./US Navy PWC) (6.7 MB)
 Video Clip of in-situ downward direct-push deployed GeoVIS moving downward beginning at the base of grassy soil surface to the top of the capillary fringe (25.7 MB/AVI) Video Clip of in-situ downward direct-push deployed GeoVIS moving downward beginning at the base of grassy soil surface to the top of the capillary fringe (25.7 MB/AVI)
 Video Clip of in-situ downward direct-push deployed GeoVIS moving downward through the capillary fringe (11.7 MB/MPG) Video Clip of in-situ downward direct-push deployed GeoVIS moving downward through the capillary fringe (11.7 MB/MPG)
 Video Clip of in-situ downward direct-push deployed GeoVIS moving into NAPL contaminated groudwater (35.7 MB/AVI) Video Clip of in-situ downward direct-push deployed GeoVIS moving into NAPL contaminated groudwater (35.7 MB/AVI)
 Accelerated VOC Source Investigation Pairing SCAPS/MIP with EPA Triad, Camp Pendleton, California (Presenter: Karen Collins, Anteon Corp./US Navy PWC) (2.4 MB) Accelerated VOC Source Investigation Pairing SCAPS/MIP with EPA Triad, Camp Pendleton, California (Presenter: Karen Collins, Anteon Corp./US Navy PWC) (2.4 MB)
 East Palo Alto Case Study: Pesticide Investigation using the Triad Approach (Presenter: Deana Crumbling, USEPA and Lily Lee, USEPA Region 9 Brownfields Program) (1.5 MB) East Palo Alto Case Study: Pesticide Investigation using the Triad Approach (Presenter: Deana Crumbling, USEPA and Lily Lee, USEPA Region 9 Brownfields Program) (1.5 MB)
 Wrap-Up & Questions (Presenter: Deana Crumbling, USEPA) (244 KB) Wrap-Up & Questions (Presenter: Deana Crumbling, USEPA) (244 KB)
Top of page
Workshops/Conferences
Triad presentations and workshops are scheduled at a variety of venues over the next several months.
- Triad Investigations: New Approaches and Innovative Strategies, Amherst, MA, June 10-12, 2008
The national conference included training sessions, workshops, and platform sessions focused on implementation of new tools, approaches, and strategies for hazardous waste site characterization, site remediation, and site redevelopment. Equipment demonstrations augmented the exhibitions to bring practical applications to the technical theory and case studies presented during the conference. The conference featured cutting edge tools and techniques for sampling and monitoring related to real-time information, continuous monitoring, and long-term monitoring for site closure and stewardship. Best practices and lessons learned were emphasized throughout the training sessions, platform sessions, and workshops
 http://www.umass.edu/tei/conferences/presentations.html
http://www.umass.edu/tei/conferences/presentations.html
Top of page
|
 |
 |